
Categories
- TRANSMISSION-LINE
- Transmission-Line Fittings
- String Hardware
- Tower Attachment
- Parallel Groove Clamp
- Suspension Clamps
- Tension Clamps
- Compression Joint
- Repair Sleeve
- Preformed Armour Rod
- Stockbridge Damper
- Spacer & Spacer Damper
- Arcing Devices
- Counterweight & Jumper weight
- Danger plate & Number plate
- Corona & Grading Rings
- Transmission Conductor
- All aluminium stranded conductors(AAC)
- Aluminium conductors steel reinforced(ACSR)
- All aluminium alloy conductors(AAAC)
- Aluminium alloy conductors steel reinforced(AACSR)
- Arial Earth Wire & Shield Wire & Galvanized Steel Wire
- Porcelain Disc Suspension Insulators
- Composite Long Rod Insulators
- Toughened Glass Disc Insulator
- Tower of Transmission-Line
- SUBSTATION
- Connector and Fittings for Tubular Busbar
- Tubular Busbar Palm(Welding)
- Busbar A-Frame
- Connector for Tubular Busbar
- Tubular Busbar Support
- Tubular Busbar Earthing
- Tubular Busbar End Caps & Balls
- Substation Insulators
- Solid Porcelain Post Insulators(66kV -500kV)
- Solid Polymer Post Insulators(66kV-500kV)
- Hollow Core Insulators for Voltage Transformer
- Hollow Core Insulators for Capacitor
- Porcelain Disc Insualtors
- Polymer Long Rod Insulators
- Glass Disc Insulators
- Busbar
- Tubular Copper Busbar
- Rectangular Aluminum Busbar
- Rectangular Copper Busbar
- Tubular Aluminum Busbar
- Terminations & Connections for Conductor
- Aluminium Flexible Connector
- Copper Flexible Connector(Flat Braid)
- Compression Run Compression T Clamp(Closed)
- Compression Run Compression T Clamp(Open)
- Compression Run Palm Tap(Closed)
- Compression Run Palm Tap(Open)
- Compression Terminal Clamp
- Twin Conductor Compression Terminal Clamp
- Straight Bolted Type Terminal Clamp
- 90° Bolted Type Terminal Clamp
- Straight Twin Conductor Bolted Type Terminal Clamp
- 90° Twin Conductor Bolted Type Terminal Clamp
- Twin Conductor Bolted Type Tee Clamp
- Twin Conductor Run Palm Tap Lengthways Terminal Clamp
- Twin Conductor Run Palm Tap Transverse Terminal Clamp
- Parallel Groove Clamp
- Straight Connector Conductor to Conductor
- Tee Connector Conductor to Conductor
- Adaptor Plates
- Straight Type
- Right Angle Horizontal Type
- Right Angle Vertical Type
- Bi-Metallic Transition Plate
- Spacers
- Galvanized & Stainless Steel Bolts Assemblies
- Strings Fittings
- Connections for Flat Busbar
- Gantries & Structure
- Distribution Conductor
- All Aluminium Stranded Conductors(AAC)
- All Aluminium Alloy Conductors(AAAC)
- Substation Parallel Spacer Triple
- DISTRIBUTION
- Preformed Fittings
- Armor-Grip Suspension Clamp
- Trunnion Armor-Grip Clamp
- Aluminum Alloy Dead-Ends
- Copper Alloy Dead-End
- Thimbles
- Top Ties
- Armored Rod Twin Ties
- Side & Spool Ties
- Parrot Bill End Aluminum Alloy Armor Rods
- Copper Alloy Armor Rods
- Galvanized Steel Armor Rods
- Aluminium Alloy Line Splice
- Copper Alloy Line Splices
- Galvanized Steel Line Splices
- Aluminium Alloy Full Tension Line Splice
- T-Connector
- Helical Arcing Horn
- Galvanized Steel Guy-Grip
- Pole Top Make Off
- Insulated Stay
- Double-Wrap Guy-Grip
- Spiral Vibration Damper High Impact PVC
- Lashing Rods
- PVC Spacer
- The Pole Line Hardware
- Cross Arms
- Fastenes Bolts & Nuts
- Thimble Bolt Rod & Eye Bolt
- Eye Nuts
- Clevis
- Insulation Pin & Studs & Spindles
- Pole Hoop
- Cable & Conductor
- ACSR
- AAC
- ABC Cable
- SAC Cable
- Distribution Insulators
- Porcelain Disc Insualtors
- Polymer Long Rod Insulators
- Glass Disc Insulators
- Porcelain Line Post Insulators(Vertical)
- Porcelain Line Post Insulators(Horizontal)
- Polymer Line Post Insulators(Vertical)
- Polymer Line Post Insulators(Horizontal)
- Porcelain Pin Insulator(BS standard)
- Porcelain Pin Insulator(ANSI standard)
- Polymer Pin Insulators
- Shackle Insulators
- Spool Insulators
- Stay Insulators
- Wiring Insulators
- Telephone Lines Insulators
- Guy Strain Insulators
- Spindle for insulators
- BS Spindle for Pin Insulators
- ANSI Spindle for Pin Insulators
- Normal Short Spindle for Line Post Insulators
- Rachet short spindle for line post insulators
- Rachet long spindle for line post insulators
- Fuse/fuse cutout
- Porcelain Fuse Cutout
- Composite Fuse Cutout
- K Type Fuse Link
- HRC Fuse
- J Type Fuse
- Disconnect Switch
- Surge Arrestor 11-36kV(5kA-10kA)
- Over head Line fittings
- Suspension Clamp
- Bolt Type Tensioning Clamp
- U-Bolts
- Shackle
- Ball Eye
- Socket Tongue
- Arcing Horn
- UT Connectors
- ABC fittings
- Copper Strand Wire and Braid Connector
- Insulation Piercing Connector(IPC)
- Fire-Retardant IPC
- T connecting Terminal
- Insulation Piercing Grounding Connectors
- Fuse Bace
- Wedged Insulation Strain Clamp
- Suspension Clamp for ABC cable
- Suspension Clamp with Aluminum Bracket
- Anchoring Clamp
- Metal Anchor Clamp
- Four-Core Tension Clamp
- Pre-Insulated Sleeve
- Pre-Insulated Bimetal Sleave
- Expansion Screws
- JXL Series Clamp(Wedge Type)
- Parallel Groove Clamp with Insulator Cover
- SAC fittings
- Anti Sway Bracket for HDPE Spacer
- Tangent Support Bracket
- HT Tape for SAC Cable
- Cable lug
- Copper Cable Lugs-DT
- Double Holes Copper Cable lugs-DT2
- Aluminum Cable Lugs-DL
- Double holes Aluminum Cable lugs-DL2
- Bi-Metal Cable Lugs-DTL
- Copper Aluminum Cable lugs-CAL-A
- Copper Aluminum Cable lugs-CAL-B
- Copper Aluminum Cable lugs-European style
- Copper Aluminum Cable lugs-For cable tap box
- Copper Cable Lugs-OT
- P.G. Clamp & Connector
- Copper Parallel Groove Clamp-CAPG
- Aluminum Parallel Groove Clamp-CAPG
- Copper Parallel Groove Clamp
- Aluminum Parallel Groove Clamp-JB
- Copper-Aluminum Parallel Groove Clamp-CAPG(Hard-Solder)
- Copper-Aluminum Parallel Groove Clamp-CAPG( Friction Welding)
- C Clamp-Copper
- C Clamp-Aluminum
- Connecting Clamp-Aluminum
- Connecting Clamp-Copper
- Connecting Clamp (Hard-Solder)
- Connecting Clamp (Friction Welding)
- Connecting Tube-Aluminum
- Connecting Tube-Copper
- Connecting Tube-Bimetal
- Copper Plate
- Aluminum Plate
- Bimetal Plate
- Copper-Aluminum Parallel Groove Clamp( Friction Welding)
- Stay complete set
- Eye Bolts
- Turn Buckle
- Thimble
- Stay Grip
- Stay Wire
- Adjustable Stay Rod
- Non Adjustable Stay Rod
- Stay Anchor Plate/Earth Plate
- Other accessory
- Stainless Steel with Retaining Buckle
- Cable Nail
- Insulation Tape
- Stainless Steel Strip
- Aluminium Insulated Tie Wire
- COMMUNICATION
- Dead-End for OPGW
- Single Suspension Set
- Double Suspension Set
- Vibration Damper
- Armour Rods for Vibration Damper
- Ground Wire Set
- Joint Box
- Cable Tray
- Spiral Vibration Damper
- Corona Coil
- Downlead
- Downlead
- Fastened Fittings for Pole
- Fastened Fittings for Pole
- Fastened Fittings for Twoer
- Fastened Fittings for Twoer
- Fastened Fittings for Twoer
- GROUNDING SYSTEM
- Earth Rod
- Solid Stainless Steel Earth Rods
- Solid Copper Earth Rods
- Copper Clad Steel Earth Rods
- H.D.G Steel Earth Rods
- Earthing Wire
- Copper Wire
- PVC Covered Copper Wire
- Flexible Copper Braid
- Copper Clad Steel Wire
- Fittings for Earth Rod
- Fittings for Threaded Earth Rod
- Fittings for Unthreaded Earth Rods
- Earth Tube
- Conductor Tape
- Copper Tape
- Tinned Copper Tape
- PVC Insulated Copper Tape
- Stainless Steel Tape
- Aluminum Tape
- Bentonite
- Concrete Earth Pits
- Connectors
- C connectors
- Tinned Copper Flexible Connector
- Tape Clip
- Tape Clamp
- Rod to Tape Clamp
- Rod to Cable Clamp
- U-Bolt Rod Clamp
- Earth Points
- Earth Plates
- Solid Copper Earth Plates
- Lattice Copper Earth Plates
- Earth Bars & Disconnector Links
- Exothermic Welding
- Exothermic Powder
- Tooling Box
- Exothermic Welding Mould
- Marconite
- INSULATOR FITTINGS
- Clevis Fittings
- Y-Clevis Fittings
- Tongue Fittings
- Socket Fittings
- Ball Fittings
- Eye Fittings
- For Line Post Insulator
- For Cross-Arm Composite Insulator
- For Pin Insulator
- For Railway Insulator
- For Clamp (Vertical)
- For Clamp (Horizontal)
- Ball Pin & Socket Cap
- Tongue Pin & Clevis Cap
- For Others
- Top Head Fitting for Line Post Insulator
- Top Head Fitting Clevis for Line Post Insulator
- Top Head fitting Tongue for Line Post Insulator
- POWER CONSTRUCTION TOOLS
- Galvanized Steel Antitwist Wire Rope
- Hydraulic Press
- Hand Hydraulic Crimping Tools
- Cable Cutter
- Tube Terminal Crimping Tools
- Mechanical Cable Cutter
- Wire Grip
- Hand Puller
- Snactch Block
- Stringing Block
- Cable Wellhead Pulley
- Cable Orifice Protection Pulleys
- High Voltage Operating Rod/Hot Stick
- H.V. Earthing Wire and Rod
- Security Clamp
- Wood Pole Climber
- Grounding Clamp
- Hot Line Cable Clamp
- Swivel Joints
- Elelctro Scope
- OEM/ODM
- SOLAR

ABC fittings
ABC fittings
-
 Copper Strand Wire and Braid Connector
Copper Strand Wire and Braid Connector● Construction: A copper braid connector is typically made by weaving or braiding multiple strands of copper wire together to form a flat, ribbon-like structure. The braiding creates a dense, flexible, and highly conductive structure.
● Flexibility: The braided structure of a copper braid connector allows it to be highly flexible, making it suitable for applications where vibration or movement is expected. It can easily conform to irregular shapes and surfaces.
● Conductivity: Copper is used due to its exceptional electrical conductivity, and the braided design ensures that the connector maintains good electrical conductivity even when subjected to mechanical stress or movement.
● Shielding: Copper braid connectors are often used for electromagnetic shielding in cables and electronic equipment. They help prevent electromagnetic interference (EMI) by creating a conductive shield around sensitive components.
● Applications: Copper braid connectors are widely used in grounding applications, electrical grounding straps, bonding cables, and for connecting various components in electrical and electronic systems.
-
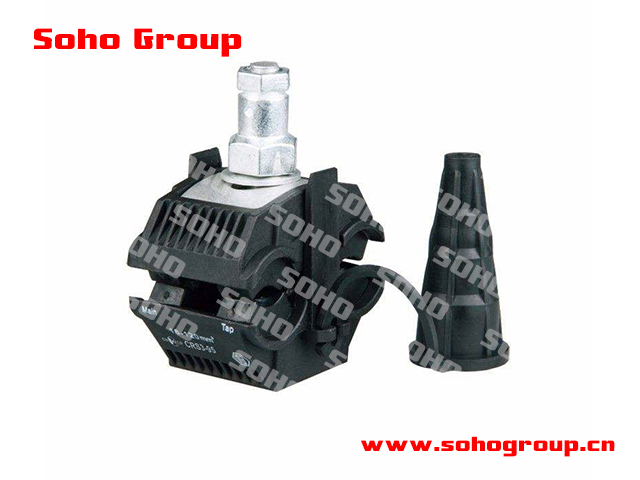 Insulation Piercing Connector(IPC)
Insulation Piercing Connector(IPC)● Piercing Teeth: The key feature of an IPC is its piercing teeth or blades, which are designed to penetrate the insulation of a conductor without damaging the conductor itself. These teeth create a secure and low-resistance electrical connection.
● Compression Mechanism: IPCs are typically equipped with a compression mechanism (often involving screws or clamps) that is used to apply pressure to the piercing teeth, ensuring a reliable connection.
● Insulation Penetration: The piercing teeth penetrate the conductor insulation to make direct contact with the conductor. This eliminates the need to strip or remove the insulation, saving time and effort during installation.
● Waterproof and Weatherproof: Many IPCs are designed to be waterproof and weatherproof, which is essential for outdoor or underground applications. They are often sealed to prevent moisture ingress and ensure long-term reliability.
● Range of Sizes: IPCs come in various sizes and configurations to accommodate different conductor diameters and insulation types. They are available for both copper and aluminum conductors.
● Multiple Ports: Some IPCs are equipped with multiple ports to allow multiple conductors to be connected within a single connector, simplifying branch connections and reducing the need for additional connectors.
● Versatility: IPCs are used for a wide range of applications, including branch connections in power distribution systems, telecommunications networks, street lighting, and more.
● Tooling: Proper installation of IPCs often requires specific tools for applying the compression force and ensuring a secure connection. The tools are typically designed to match the specific connector type and size.
● Reliability: When installed correctly, IPCs provide reliable and low-resistance electrical connections, reducing the risk of loose connections or overheating.
● Safety: Using IPCs eliminates the need for stripping insulation, reducing the risk of accidental contact with live conductors during installation.
-
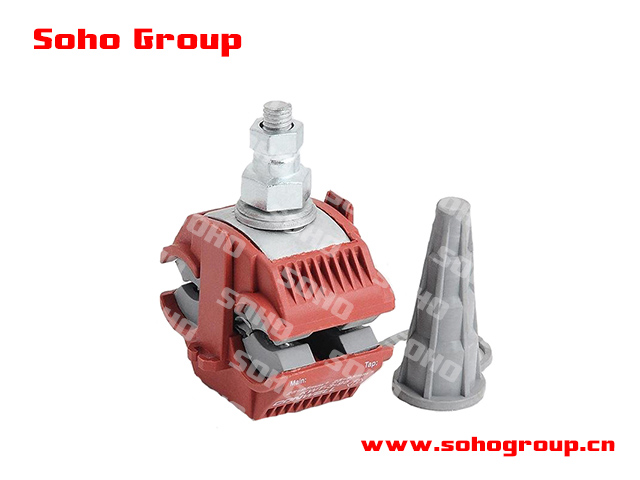 Fire-Retardant IPC
Fire-Retardant IPCA fire-retardant insulation piercing connector is a specialized type of insulation piercing connector (IPC) designed to maintain its integrity and electrical performance even in the presence of fire. These connectors are crucial in applications where fire resistance is a critical requirement, such as fire-resistant electrical cables and circuits in buildings.
Fire-Resistant Material:
● Construction - Fire-retardant IPCs are constructed using materials that are resistant to flames and heat. This often includes special fire-resistant plastics or insulating materials that are designed to withstand high temperatures and prevent the spread of fire.
● Flame Resistance - These connectors are tested and certified to meet specific flame resistance standards and are intended to maintain their electrical functionality even in the presence of a fire.
-
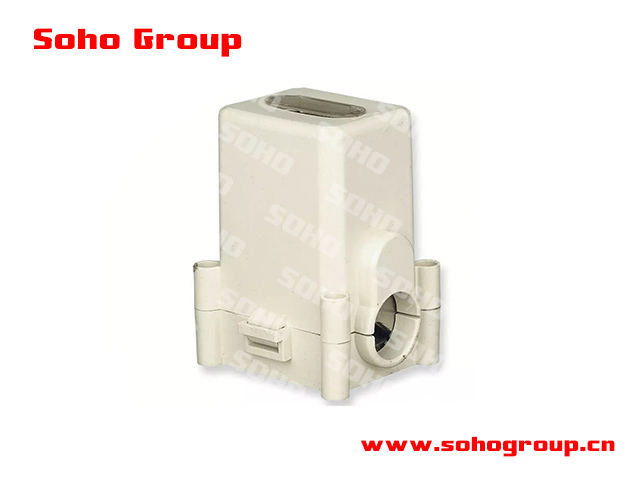 T connecting Terminal
T connecting TerminalT connecting terminals for ABC are used to connect or branch ABC conductors in overhead power distribution networks.
● Design: These connectors are designed in a "T" shape, with one end of the T connecting to the main conductor, and the top of the T allowing for the attachment of a branch conductor.
● Materials: They are typically made from corrosion-resistant materials, such as aluminum or copper, to ensure long-lasting performance in outdoor environments.
● Secure Connection: T connecting terminals are designed to provide a secure and low-resistance electrical connection between the main conductor and the branch conductor without damaging the insulation of the ABC cables.
● Installation: Proper installation of T connecting terminals often involves using specialized tools and hardware to ensure a tight and reliable connection. The connectors are typically crimped or compressed onto the conductors.
● Weatherproofing Some T connecting terminals come with weatherproofing features to protect the connection from moisture and environmental factors, ensuring long-term reliability.
● Versatility: These connectors can be used in various configurations to accommodate different branching and connection requirements in ABC systems, such as T-offs, Y-offs, and straight-line connections.
● Standards and Codes: The design and application of T connecting terminals for ABC should comply with relevant electrical codes and standards to ensure safety and reliability in distribution systems.
-
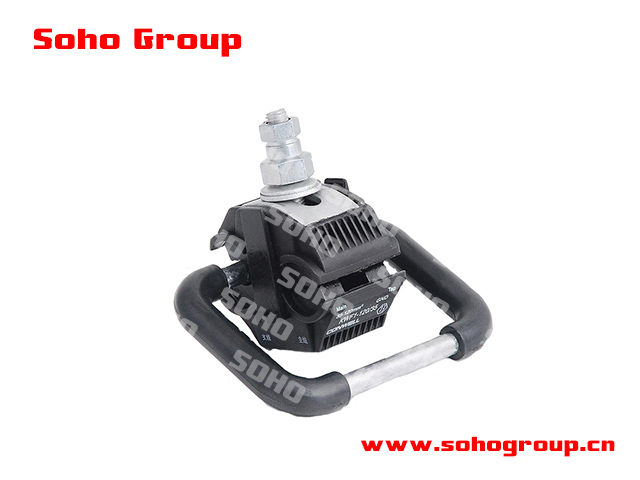 Insulation Piercing Grounding Connectors
Insulation Piercing Grounding Connectors● Insulation Piercing Design:IPGCs are equipped with piercing teeth or blades that can penetrate the insulation of the conductor to establish a direct, low-resistance connection with the conductor itself.
● Grounding and Bonding: IPGCs are primarily used for grounding and bonding applications. They provide a reliable connection between grounding conductors, grounding electrodes, or other components of a grounding system.
● Compression Mechanism: These connectors often incorporate a compression mechanism, which can be screw-based or involve other fastening methods, to apply pressure to the piercing teeth, ensuring a secure electrical connection.
● Versatility: IPGCs come in various sizes and configurations to accommodate different conductor diameters and grounding requirements. They are available for both copper and aluminum conductors.
● Weatherproofing: Many IPGCs are designed to be weatherproof and corrosion-resistant to ensure long-term performance in outdoor or exposed environments.
● Environmental Resistance: They are designed to withstand environmental factors, including moisture and UV exposure, to maintain their integrity and electrical performance.
● Wide Range of Applications: IPGCs are commonly used in utility pole grounding, telecommunications grounding, bonding of grounding electrodes, and other electrical grounding systems.
● Code Compliance: Proper selection and installation of IPGCs should comply with relevant electrical codes and standards specific to grounding and bonding applications.
● Safety: IPGCs play a critical role in ensuring the safety of electrical systems and personnel by providing a reliable ground connection, helping to prevent electrical faults and overvoltages.
-
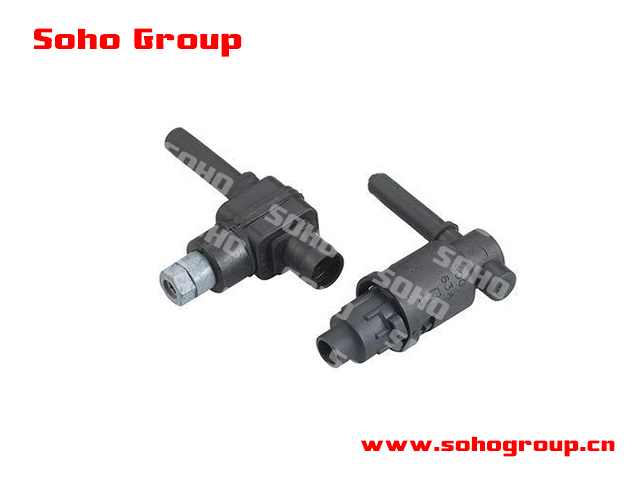 Fuse Bace
Fuse Bace● Secure Mounting: Fuse bases provide a secure and standardized mounting for fuses, ensuring that they are properly positioned within an electrical circuit.
● Compatibility: Fuse bases are designed to accommodate specific types and ratings of fuses, including different physical sizes, voltage ratings, and current-carrying capacities.
● Electrical Contacts: The fuse base typically contains electrical contacts that connect to the fuse elements. When a fuse is properly inserted into the base, it forms an electrical connection between the circuit and the load, allowing current to flow.
● Material: Fuse bases are typically constructed from materials with good electrical conductivity and mechanical strength, such as brass or other metal alloys.
● Types: Fuse bases come in various types, including panel mount bases, rail-mounted bases, and socket bases, among others. The type of base used depends on the specific application and how the fuse holder is installed in the system.
● Mounting Methods: Fuse bases can be mounted directly onto a panel, on a DIN rail, or within an electrical enclosure, depending on the installation requirements.
● Safety: Fuse bases are an essential component for electrical safety. They ensure that fuses are properly installed and protect against electrical faults, overloads, and short circuits.
● Disconnecting Capability: : In some applications, fuse bases may have disconnecting capabilities that allow for the isolation of the circuit before replacing a fuse. This is especially important for safety during maintenance and servicing.
● Reusability: Some fuse bases allow for the replacement and reuse of fuses after a fault has occurred, while others are designed for one-time use.
● Code Compliance: Proper selection and installation of fuse bases should comply with relevant electrical codes and standards to ensure the safety and reliability of the electrical system.
-
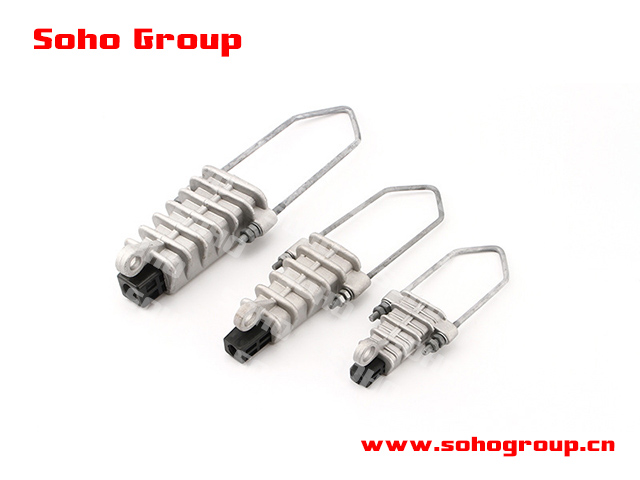 Wedged Insulation Strain Clamp
Wedged Insulation Strain Clamp● Insulation Support: Wedged insulation strain clamps are designed to provide support and tension for insulated conductors or cables. They are used to secure the cable in place while maintaining electrical insulation.
● Wedge Design: The key feature of these clamps is the wedge-shaped design that grips the cable. The wedge mechanism exerts a clamping force on the cable, holding it securely in position.
● Materials: Wedged insulation strain clamps are typically made of corrosion-resistant materials such as aluminum or other non-ferrous alloys to ensure long-lasting performance in outdoor environments.
● Insulation Protection: These clamps are designed to maintain the integrity of the insulation on the cable, preventing it from being damaged or compromised.
● Multiple Sizes: Wedged insulation strain clamps are available in various sizes to accommodate different cable diameters and configurations. Proper selection is essential to ensure a secure fit.
● Installation: Installation of these clamps typically involves mounting them on a supporting structure, such as a utility pole or tower, and attaching the cable securely using the wedge mechanism.
● Strain Relief: Wedged insulation strain clamps are used to relieve mechanical stress or tension on the cable. They help prevent the cable from moving or sagging under the influence of wind, temperature changes, or other factors.
● Weatherproofing: Many wedged insulation strain clamps are designed to be weatherproof and resistant to environmental factors, ensuring reliable performance over time.
● Electrical Safety: These clamps contribute to the safety and reliability of electrical distribution systems by preventing sagging or undue stress on cables, reducing the risk of mechanical failure or electrical faults.
● Code Compliance: Proper selection and installation of wedged insulation strain clamps should comply with relevant electrical codes and standards to ensure safety and reliability in the distribution system.
-
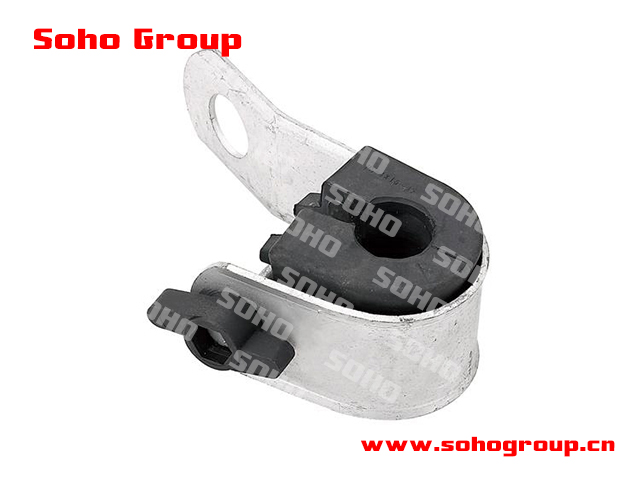 Suspension Clamp for ABC cable
Suspension Clamp for ABC cable● Application: Suspension clamps for ABC are specifically designed to provide support and tension for ABC cables in overhead power distribution systems. They are used to secure and suspend the bundled cable between support structures like utility poles or towers.
● Design: Suspension clamps are designed to accommodate the specific configuration of ABC cables. They typically feature a combination of grooves, grips, and attachments to hold the bundled cable securely.
● Materials: These clamps are often constructed from corrosion-resistant materials such as aluminum or stainless steel to withstand outdoor and environmental conditions.
● Insulation Protection: Suspension clamps are designed to protect the integrity of the insulation on the ABC cable, ensuring that the cable is securely held without damage.
● Tension Relief: They provide mechanical support and tension relief for the ABC cable, preventing sagging or excessive stress on the cable due to wind, temperature variations, or other factors.
● Installation: Installation of suspension clamps typically involves attaching them to supporting structures (such as utility poles) using appropriate hardware, and then securing the ABC cable in the clamp. Proper tensioning is essential to maintain the integrity of the cable.
● Weatherproofing: Many suspension clamps are designed to be weatherproof and resistant to environmental factors to ensure long-term reliability.
● Electrical Safety: Suspension clamps contribute to the safety and reliability of overhead power distribution systems by preventing sagging, reducing the risk of mechanical failure, and maintaining proper clearances.
● Code Compliance: Proper selection and installation of suspension clamps should comply with relevant electrical codes, regulations, and industry standards to ensure safety and reliability in the power distribution system.
● Versatility: Suspension clamps for ABC come in various sizes and configurations to accommodate different cable diameters and configurations.
-
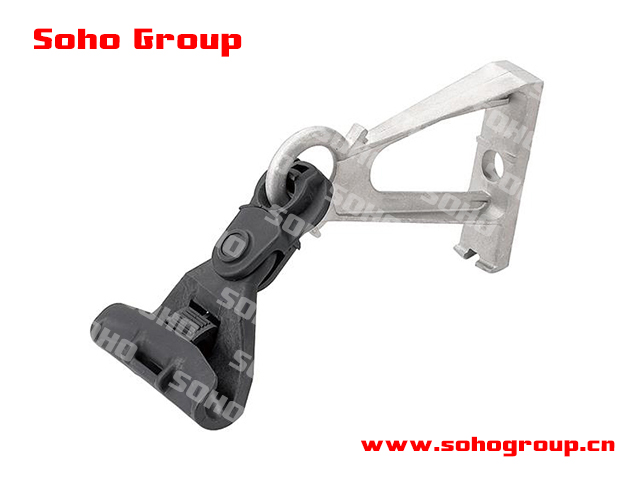 Suspension Clamp with Aluminum Bracket
Suspension Clamp with Aluminum Bracket● Application: Suspension clamps for ABC are specifically designed to provide support and tension for ABC cables in overhead power distribution systems. They are used to secure and suspend the bundled cable between support structures like utility poles or towers.
● Design: Suspension clamps are designed to accommodate the specific configuration of ABC cables. They typically feature a combination of grooves, grips, and attachments to hold the bundled cable securely.
● Materials: These clamps are often constructed from corrosion-resistant materials such as aluminum or stainless steel to withstand outdoor and environmental conditions.
● Insulation Protection: Suspension clamps are designed to protect the integrity of the insulation on the ABC cable, ensuring that the cable is securely held without damage.
● Tension Relief: They provide mechanical support and tension relief for the ABC cable, preventing sagging or excessive stress on the cable due to wind, temperature variations, or other factors.
● Installation: Installation of suspension clamps typically involves attaching them to supporting structures (such as utility poles) using appropriate hardware, and then securing the ABC cable in the clamp. Proper tensioning is essential to maintain the integrity of the cable.
● Weatherproofing: Many suspension clamps are designed to be weatherproof and resistant to environmental factors to ensure long-term reliability.
● Electrical Safety: Suspension clamps contribute to the safety and reliability of overhead power distribution systems by preventing sagging, reducing the risk of mechanical failure, and maintaining proper clearances.
● Code Compliance: Proper selection and installation of suspension clamps should comply with relevant electrical codes, regulations, and industry standards to ensure safety and reliability in the power distribution system.
● Versatility: Suspension clamps for ABC come in various sizes and configurations to accommodate different cable diameters and configurations.
-
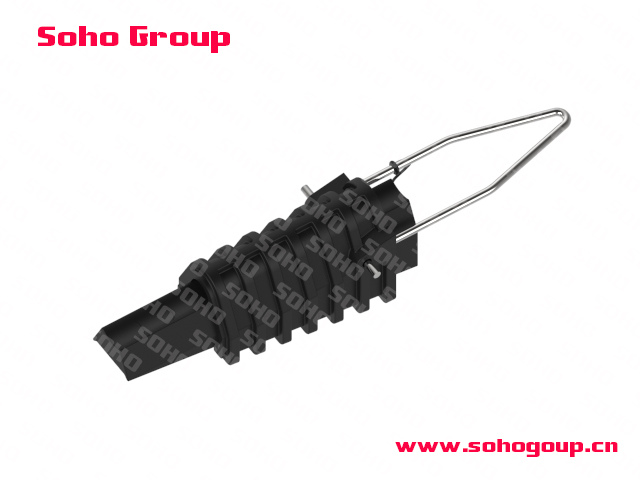 Anchoring Clamp
Anchoring Clamp● Application: Anchoring clamps for ABC are specifically designed to anchor or secure the bundled cable in place, preventing sagging, undue mechanical stress, and maintaining the proper clearances in overhead power distribution systems.
● Design: These clamps are designed to accommodate the specific configuration of ABC cables. They typically feature grooves, grips, or other mechanisms that securely hold the bundled cable in place.
● Materials: Anchoring clamps are often constructed from corrosion-resistant materials such as aluminum, stainless steel, or other non-ferrous alloys to ensure durability and resistance to outdoor and environmental conditions.
● Insulation Protection: Anchoring clamps are designed to protect the integrity of the insulation on the ABC cable, ensuring that the cable is securely held without damage.
● Tension Relief: They provide mechanical support and tension relief for the ABC cable, preventing sagging or excessive stress on the cable due to wind, temperature variations, or other factors.
● Tension Relief: Installation of anchoring clamps involves attaching them to supporting structures, such as utility poles or buildings, using appropriate hardware and then securing the ABC cable in the clamp. Proper tensioning is essential to maintain the integrity of the cable.
● Weatherproofing: Many anchoring clamps are designed to be weatherproof and resistant to environmental factors to ensure long-term reliability.
● Electrical Safety: Anchoring clamps contribute to the safety and reliability of overhead power distribution systems by preventing sagging, reducing the risk of mechanical failure, and maintaining proper clearances.
● Electrical Safety: Proper selection and installation of anchoring clamps should comply with relevant electrical codes, regulations, and industry standards to ensure safety and reliability in the power distribution system.
● Versatility: Anchoring clamps for ABC come in various sizes and configurations to accommodate different cable diameters and configurations.
-
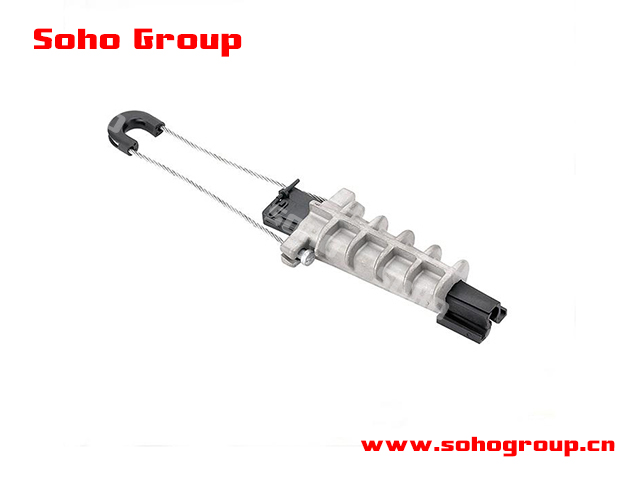 Metal Anchor Clamp
Metal Anchor Clamp● Application: Anchoring clamps for ABC are specifically designed to anchor or secure the bundled cable in place, preventing sagging, undue mechanical stress, and maintaining the proper clearances in overhead power distribution systems.
● Design: These clamps are designed to accommodate the specific configuration of ABC cables. They typically feature grooves, grips, or other mechanisms that securely hold the bundled cable in place.
● Materials: Anchoring clamps are often constructed from corrosion-resistant materials such as aluminum, stainless steel, or other non-ferrous alloys to ensure durability and resistance to outdoor and environmental conditions.
● Insulation Protection: Anchoring clamps are designed to protect the integrity of the insulation on the ABC cable, ensuring that the cable is securely held without damage.
● Tension Relief: They provide mechanical support and tension relief for the ABC cable, preventing sagging or excessive stress on the cable due to wind, temperature variations, or other factors.
● Tension Relief: Installation of anchoring clamps involves attaching them to supporting structures, such as utility poles or buildings, using appropriate hardware and then securing the ABC cable in the clamp. Proper tensioning is essential to maintain the integrity of the cable.
● Weatherproofing: Many anchoring clamps are designed to be weatherproof and resistant to environmental factors to ensure long-term reliability.
● Electrical Safety: Anchoring clamps contribute to the safety and reliability of overhead power distribution systems by preventing sagging, reducing the risk of mechanical failure, and maintaining proper clearances.
● Electrical Safety: Proper selection and installation of anchoring clamps should comply with relevant electrical codes, regulations, and industry standards to ensure safety and reliability in the power distribution system.
● Versatility: Anchoring clamps for ABC come in various sizes and configurations to accommodate different cable diameters and configurations.
-
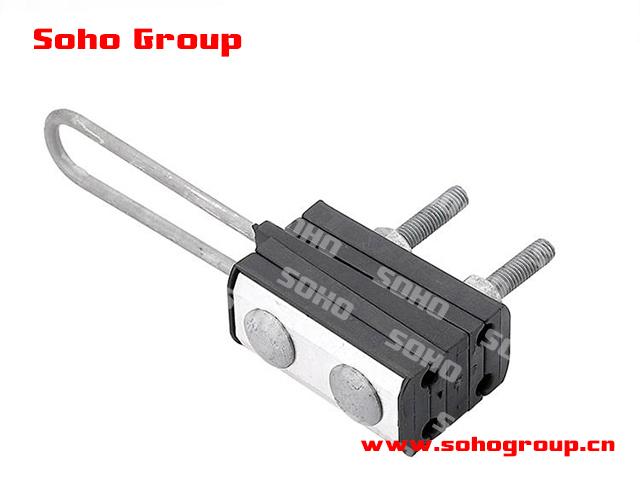 Four-Core Tension Clamp
Four-Core Tension Clamp● Application: Anchoring clamps for ABC are specifically designed to anchor or secure the bundled cable in place, preventing sagging, undue mechanical stress, and maintaining the proper clearances in overhead power distribution systems.
● Design: These clamps are designed to accommodate the specific configuration of ABC cables. They typically feature grooves, grips, or other mechanisms that securely hold the bundled cable in place.
● Materials: Anchoring clamps are often constructed from corrosion-resistant materials such as aluminum, stainless steel, or other non-ferrous alloys to ensure durability and resistance to outdoor and environmental conditions.
● Insulation Protection: Anchoring clamps are designed to protect the integrity of the insulation on the ABC cable, ensuring that the cable is securely held without damage.
● Tension Relief: They provide mechanical support and tension relief for the ABC cable, preventing sagging or excessive stress on the cable due to wind, temperature variations, or other factors.
● Tension Relief: Installation of anchoring clamps involves attaching them to supporting structures, such as utility poles or buildings, using appropriate hardware and then securing the ABC cable in the clamp. Proper tensioning is essential to maintain the integrity of the cable.
● Weatherproofing: Many anchoring clamps are designed to be weatherproof and resistant to environmental factors to ensure long-term reliability.
● Electrical Safety: Anchoring clamps contribute to the safety and reliability of overhead power distribution systems by preventing sagging, reducing the risk of mechanical failure, and maintaining proper clearances.
● Electrical Safety: Proper selection and installation of anchoring clamps should comply with relevant electrical codes, regulations, and industry standards to ensure safety and reliability in the power distribution system.
● Versatility: Anchoring clamps for ABC come in various sizes and configurations to accommodate different cable diameters and configurations.
-
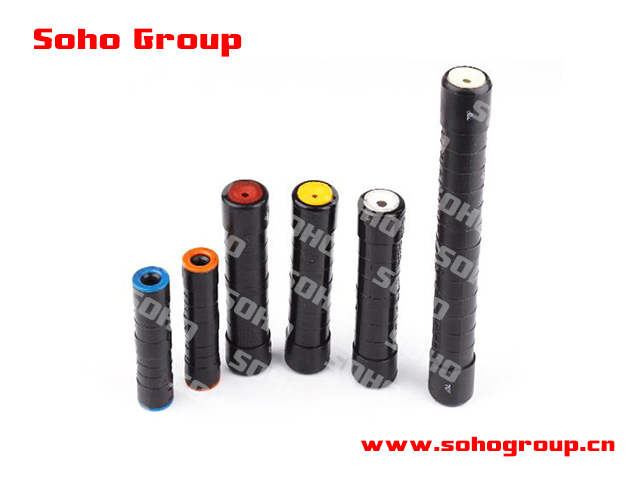 Pre-Insulated Sleeve
Pre-Insulated Sleeve● Insulation: The primary function of a pre-insulated sleeve is to provide electrical insulation. It is made of insulating materials such as heat-shrinkable polyolefin, PVC, or other plastics that protect against electrical contact.
● Tubular Design: Pre-insulated sleeves are typically tubular in shape and can be slipped over a wire termination or connection, covering it completely.
● Heat-Shrinkable: Some pre-insulated sleeves are heat-shrinkable, meaning they can be heated to shrink and conform to the shape of the underlying termination or connection, providing a snug fit and a secure seal.
● Crimpable: Others are crimpable, meaning they can be crimped onto the wire termination using appropriate crimping tools to secure them in place.
● Color-Coding: Pre-insulated sleeves are often color-coded to help identify wire connections, ensuring that the correct wires are joined and connected.
● Sizes and Types: They come in various sizes and types to accommodate different wire sizes, connection types, and insulation requirements.
● Weather Resistance: Many pre-insulated sleeves are designed to be weather-resistant, offering protection against moisture, corrosion, and environmental factors. This is especially important for outdoor or harsh environment applications.
● Terminal Protection: Pre-insulated sleeves protect wire terminations from physical damage, abrasion, and exposure, which can lead to electrical faults and hazards.
● Electrical Safety: These sleeves enhance electrical safety by preventing accidental contact with live conductors and reducing the risk of electrical faults.
● Automotive and Wiring Applications: Pre-insulated sleeves are commonly used in automotive wiring, electrical installations, and various applications where wire connections need to be protected and insulated.
● Customization: Some pre-insulated sleeves can be customized with printed labels or markings for easy identification and labeling of wire connections.
-
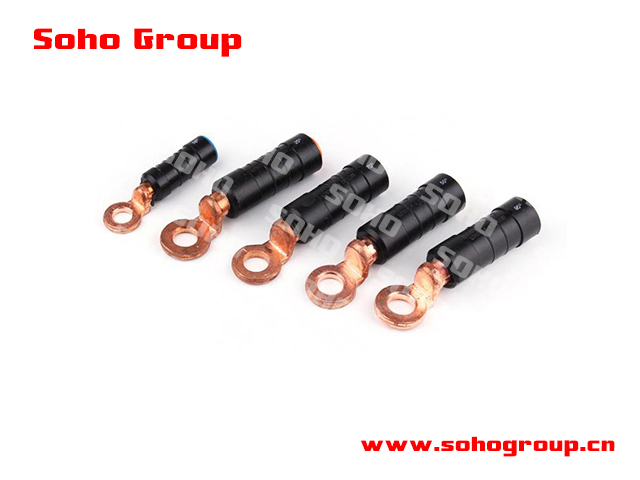 Pre-Insulated Bimetal Sleave
Pre-Insulated Bimetal Sleave● Bimetal Construction: Pre-insulated bimetal sleeves are constructed from two different metals, typically copper and aluminum, joined together to create a reliable electrical connection. The two metals are chosen for their electrical properties and compatibility.
● Insulation: These sleeves are equipped with insulation materials, often made of heat-shrinkable polyolefin or other insulating materials, that cover and protect the bimetallic connection. This insulation provides electrical and thermal protection.
● Electrical Transition: Pre-insulated bimetal sleeves are designed to facilitate the transition between different conductive materials, such as copper to aluminum, while maintaining good electrical conductivity.
● Heat Shrinkable: Many pre-insulated bimetal sleeves are heat-shrinkable, meaning they can be heated to shrink and conform to the underlying conductors, creating a secure and insulated connection.
● Sizes and Types: These sleeves come in various sizes and types to accommodate different wire sizes and connection requirements.
● Corrosion Resistance: Bimetallic connections can be susceptible to galvanic corrosion, so the insulation and design of the sleeves help prevent this by isolating the metals from each other.
● Weather Resistance: Many pre-insulated bimetal sleeves are designed to be weather-resistant, offering protection against moisture and environmental factors, making them suitable for outdoor applications.
● Electrical Safety: These sleeves enhance electrical safety by providing insulation, preventing short circuits or accidental contact with live conductors.
● Thermal Performance: In addition to electrical insulation, some sleeves also offer thermal insulation, which can be beneficial in applications where temperature variations are a concern.
● Application: Pre-insulated bimetal sleeves are commonly used in power distribution and electrical installations, particularly in situations where copper and aluminum conductors need to be securely joined and insulated.
-
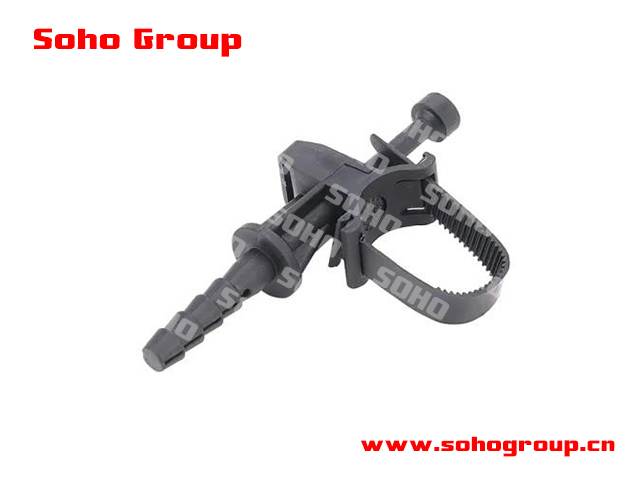 Expansion Screws
Expansion Screws● Types of Expansion Screws: There are several types of expansion screws, each with a specific design and function. Some common types include wedge anchors, sleeve anchors, and drop-in anchors. The choice of expansion screw type depends on the application and the type of material being anchored.
● Expansion Mechanism: Expansion screws have an expansion mechanism that allows them to create a secure connection with the base material. This mechanism often involves the use of a conical or wedge-shaped component that expands as the screw is tightened, providing a secure grip.
● Base Materials: Expansion screws are suitable for use in solid materials like concrete, brick, block, and stone. The base material must be dense and solid to ensure proper anchor performance.
● Installation: Installation typically involves drilling a hole into the base material, inserting the expansion screw into the hole, and tightening it using a wrench or other suitable tool. As the screw tightens, the expansion component expands, creating a secure attachment.
● Load Capacity: The load capacity of an expansion screw depends on factors like the type of anchor, the size of the hole, and the material's strength. Manufacturers provide load capacity data for specific anchor types and sizes.
● Corrosion Resistance: Some expansion screws are made of materials that resist corrosion, making them suitable for use in outdoor or corrosive environments.
● Materials: Expansion screws are commonly made from materials like steel, stainless steel, and other metals.
● Versatility: Expansion screws are versatile and can be used to secure a wide range of objects, including shelving, brackets, electrical conduit, and equipment to walls or ceilings.
● Removal: While expansion screws provide a secure attachment, they are typically not designed for easy removal. Removing them may damage the base material, so careful consideration is needed when choosing their use.
● Safety: Proper installation of expansion screws is essential to ensure safety and reliability. Following manufacturer guidelines and recommendations is crucial for secure anchoring.
-
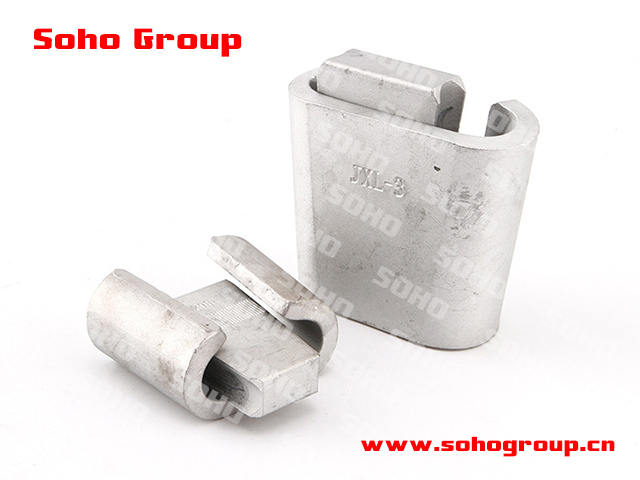 JXL Series Clamp(Wedge Type)
JXL Series Clamp(Wedge Type)● Application: The JXL Series clamp or wedge-type clamp is used to secure and support conductors or cables in overhead electrical distribution systems, such as those found on utility poles or towers.
● Wedge-Type Design: The key feature of these clamps is their wedge-shaped design, which exerts pressure on the conductor, holding it securely in place. This wedge mechanism provides a strain-relieved connection.
● Materials: JXL Series clamps are typically constructed from corrosion-resistant materials such as aluminum, ensuring their durability and resistance to environmental factors.
● Versatility: These clamps come in various sizes and configurations to accommodate different conductor diameters and configurations, making them suitable for a range of applications.
● Weatherproofing: Many JXL Series clamps are designed to be weatherproof and resistant to environmental factors, ensuring long-term reliability, particularly in outdoor environments.
● Installation: Installation typically involves attaching the clamp to supporting structures, such as utility poles or towers, and securing the conductor or cable in the clamp using the wedge mechanism. Proper tensioning is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the connection.
● Electrical Safety: JXL Series clamps play a vital role in enhancing electrical safety by preventing conductor movement, reducing the risk of mechanical failure or electrical faults, and maintaining proper clearances.
● Code Compliance: Proper selection and installation of JXL Series clamps should comply with relevant electrical codes and standards to ensure safety and reliability in the power distribution system.
-
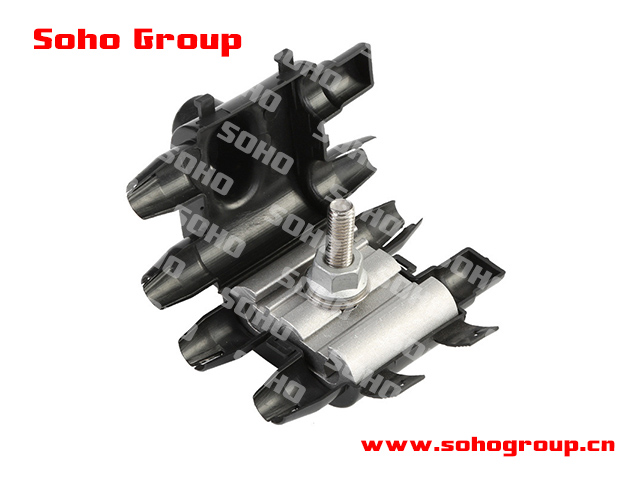 Parallel Groove Clamp with Insulator Cover
Parallel Groove Clamp with Insulator Cover● Application: Parallel groove clamps with insulator covers are commonly used in overhead power distribution systems to connect conductors or cables securely while isolating them from each other and the supporting structure, such as a utility pole or tower.
● Parallel Grooves: The term "parallel groove" refers to the design of the clamp, which typically features grooves or channels where conductors are placed and secured. These grooves ensure proper alignment and contact with the conductor.
● Materials: These clamps are often constructed from materials like aluminum, copper, or other metals with suitable electrical and mechanical properties, and the insulator cover is typically made of non-conductive materials like polymers or plastics.
● Insulation Cover: The insulator cover is a key feature, providing electrical insulation to prevent direct contact between the conductor and the clamp, as well as isolation between multiple conductors.
● Weatherproofing: Many parallel groove clamps with insulator covers are designed to be weatherproof and resistant to environmental factors, ensuring long-term reliability, especially in outdoor environments.
● Load Capacity: These clamps are designed to accommodate various conductor sizes and types, with load capacity ratings determined by the manufacturer.
● Installation: Installation involves placing the conductors in the parallel grooves and securing them with bolts or other fasteners. The insulator cover is then installed to provide electrical insulation.
● Electrical Safety: The insulator cover plays a crucial role in enhancing electrical safety by preventing direct contact between the conductor and the clamp, as well as between conductors. This reduces the risk of electrical faults and accidents.
● Code Compliance: Proper selection and installation of parallel groove clamps with insulator covers should comply with relevant electrical codes and standards to ensure safety and reliability in the power distribution system.
Sorry, no matches were found in Products for ABC fittings.
Want to get the matched products and detailed quotations?







 +86-25-58065309
+86-25-58065309
 www.sohogroup.cn
www.sohogroup.cn Daqiao Industry Park, Yangzhou City,
Daqiao Industry Park, Yangzhou City,